Understanding Liquidity in DeFi and Horizen EON’s Approach
TL;DR
- Essence of DeFi Liquidity: Liquidity in Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is crucial for enabling seamless asset conversion, ensuring market depth and health, and facilitating price discovery and stability. This liquidity is vital for the success of various DeFi innovations like yield farming and lending protocols.
- Mechanisms and Challenges of Liquidity in DeFi: Liquidity in DeFi is primarily facilitated through liquidity pools, automated market makers (AMMs), and the role of liquidity providers (LPs). However, it faces challenges like impermanent loss and the need for cross-protocol liquidity to enhance ecosystem utility.
- Horizen EON's Approach to Enhancing Liquidity: Horizen EON, an EVM-compatible platform, enhances DeFi liquidity through strategic partnerships, leveraging Ethereum's liquidity, and advanced smart contract functionalities. It focuses on developer and community empowerment, embracing novel DeFi solutions, and prioritizing security and risk management to foster a robust liquidity environment.
Introduction
Liquidity stands as a cornerstone in the dynamic world of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), essential for the seamless execution of trades and financial activities. But what exactly is liquidity in the DeFi context, and how does it function? Moreover, how is Horizen's EVM-compatible smart contracting platform, EON, playing a pivotal role in enabling liquidity? This article delves into the intricacies of DeFi liquidity, its mechanisms, and Horizen EON's unique approach.
What is Liquidity in DeFi?
Liquidity in the realm of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is a multifaceted concept, pivotal to its operations and growth. It's not just about the ability to quickly convert assets without significant price impact, but also about ensuring that the DeFi ecosystem remains efficient, inclusive, and secure.
- Seamless Asset Conversion: At its core, liquidity in DeFi refers to the ease with which assets can be swapped or traded. High liquidity ensures that assets like cryptocurrencies and tokens can be quickly exchanged with minimal slippage - the difference between expected and actual trade prices.
- Market Depth and Health: Liquidity is also an indicator of a market’s depth and health. In a highly liquid market, a large volume of assets can be traded without causing major price fluctuations, signifying a robust and stable environment.
- Price Discovery and Stability: Liquidity facilitates efficient price discovery, ensuring that asset prices reflect true market values based on supply and demand. This stability attracts more participants, creating a virtuous cycle of increased liquidity.
- Impact on DeFi Innovations: Liquidity affects the feasibility and success of various DeFi innovations. Whether it's yield farming, lending protocols, or synthetic assets, each relies on adequate liquidity to function effectively and attract users.
How Does Liquidity Work in DeFi?
The mechanisms of liquidity in DeFi are intricate and diverse, reflecting the innovation at the heart of this sector.
Liquidity Pools: Central to DeFi liquidity are liquidity pools, where users lock their assets into smart contracts. These pools act as decentralized marketplaces, enabling activities like swapping, lending, or yield farming.

Role of Liquidity Providers (LPs): Users who deposit their assets into these pools are known as Liquidity Providers. They are incentivized through transaction fees or interest from borrowers. In some protocols, they also receive governance tokens, which confer voting rights and a stake in the protocol’s future.
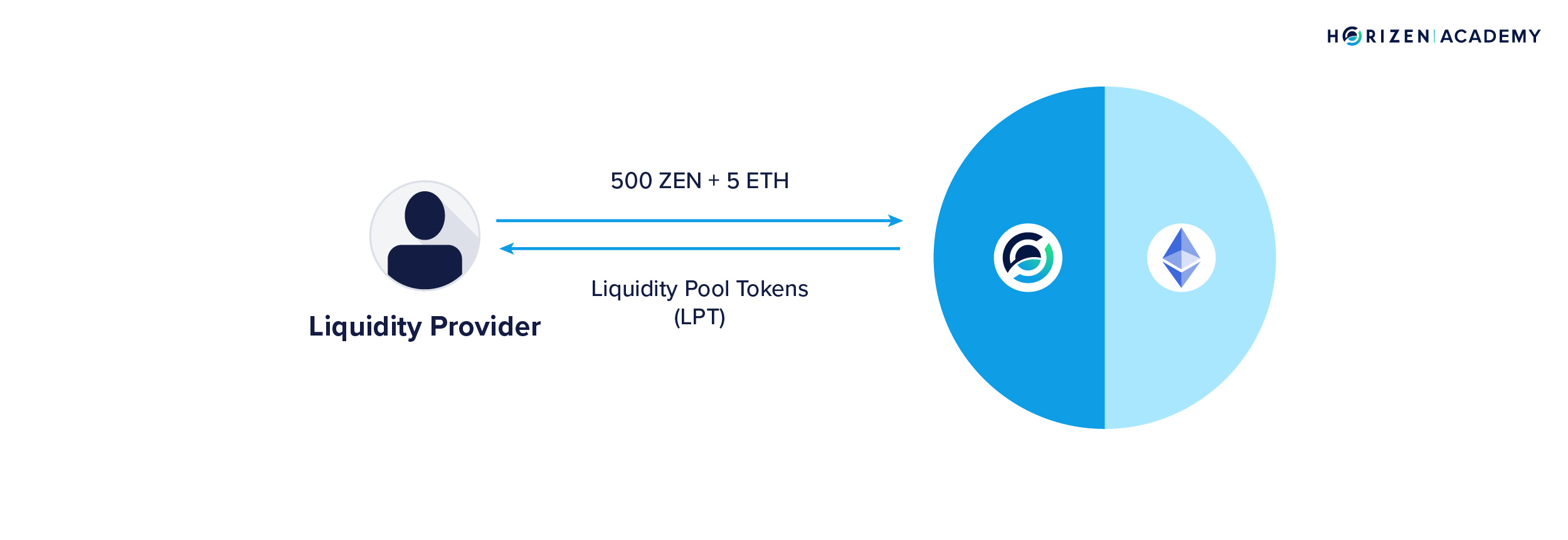
Automated Market Makers (AMMs): A significant innovation in DeFi, AMMs replace traditional order books with pre-funded liquidity pools for asset trading. They use algorithms to determine prices based on the asset's supply in the pool, facilitating continuous and automated trading.
Dynamic Liquidity Provision: Unlike traditional finance, where market makers are often institutional players, DeFi allows anyone to become a liquidity provider. This democratization leads to a more distributed and potentially resilient liquidity provision system.
Risk Management: Liquidity provision in DeFi is not without risks, including impermanent loss, where the value of deposited assets changes unfavorably compared to holding them. Advanced DeFi platforms incorporate strategies and mechanisms to mitigate these risks.
Cross-Protocol Liquidity: DeFi protocols are increasingly interoperable, allowing liquidity to flow between different systems. This cross-protocol interaction enhances overall liquidity and utility in the DeFi ecosystem.
Different Ways of Providing Liquidity in DeFi Apps
The DeFi landscape offers several innovative mechanisms for providing liquidity. These mechanisms are crucial for the functionality of DeFi applications, ensuring users can efficiently execute transactions. Here's a view of the various methods used to offer liquidity in DeFi applications:
Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
Functioning:
AMMs, a revolutionary concept in DeFi, automate the trading process using liquidity pools instead of traditional order books. In this model, the price of assets is determined algorithmically, based on the ratio of assets in the pool. Users contribute assets to these pools and receive liquidity provider (LP) tokens in return, representing their share of the pool.
Pros:
- Accessibility: AMMs lower entry barriers for liquidity providers, allowing anyone to contribute regardless of the size of their assets.
- Price Stability: They facilitate better price stability in smaller or newer markets, which might not attract market makers in traditional systems.
- Incentives: Liquidity providers earn a portion of transaction fees, which can be a stable source of passive income.
Cons:
- Impermanent Loss Risks: Significant price volatility can lead to losses for liquidity providers, as the value of their deposited assets changes in relation to one another.
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Being entirely dependent on smart contracts, AMMs are susceptible to bugs and exploits, which can lead to substantial financial losses.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Functioning:
DEXs allow users to trade cryptocurrencies directly from their wallets, without an intermediary. They use smart contracts to facilitate trading, and liquidity is provided by users themselves, often through AMMs.
Pros:
- Enhanced Security: Users maintain control of their funds, reducing the risk of exchange hacks.
- Greater Transparency: All transactions are recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and auditability.
- No KYC Requirements: DEXs typically don’t require Know Your Customer (KYC) processes, preserving user privacy.
Cons:
- Limited Liquidity for Some Pairs: Not all trading pairs have sufficient liquidity, leading to higher slippage costs.
- User Experience: Can be less user-friendly, especially for those new to the crypto space.
- Network Congestion: High network usage can lead to slower transactions and higher fees.
Yield Farming and Staking
Functioning:
In yield farming, users lock up their cryptocurrencies to receive rewards. These rewards can be in the form of transaction fees, interest from lenders, or a distribution of new tokens. Staking involves holding funds in a cryptocurrency wallet to support the operations of a blockchain network.
Pros:
- Higher Returns: Potentially offers higher returns compared to traditional financial instruments.
- Network Support: Staking helps in maintaining the security and efficiency of blockchain networks.
- Diverse Opportunities: A wide range of platforms and protocols offer different yield farming strategies to suit various risk appetites.
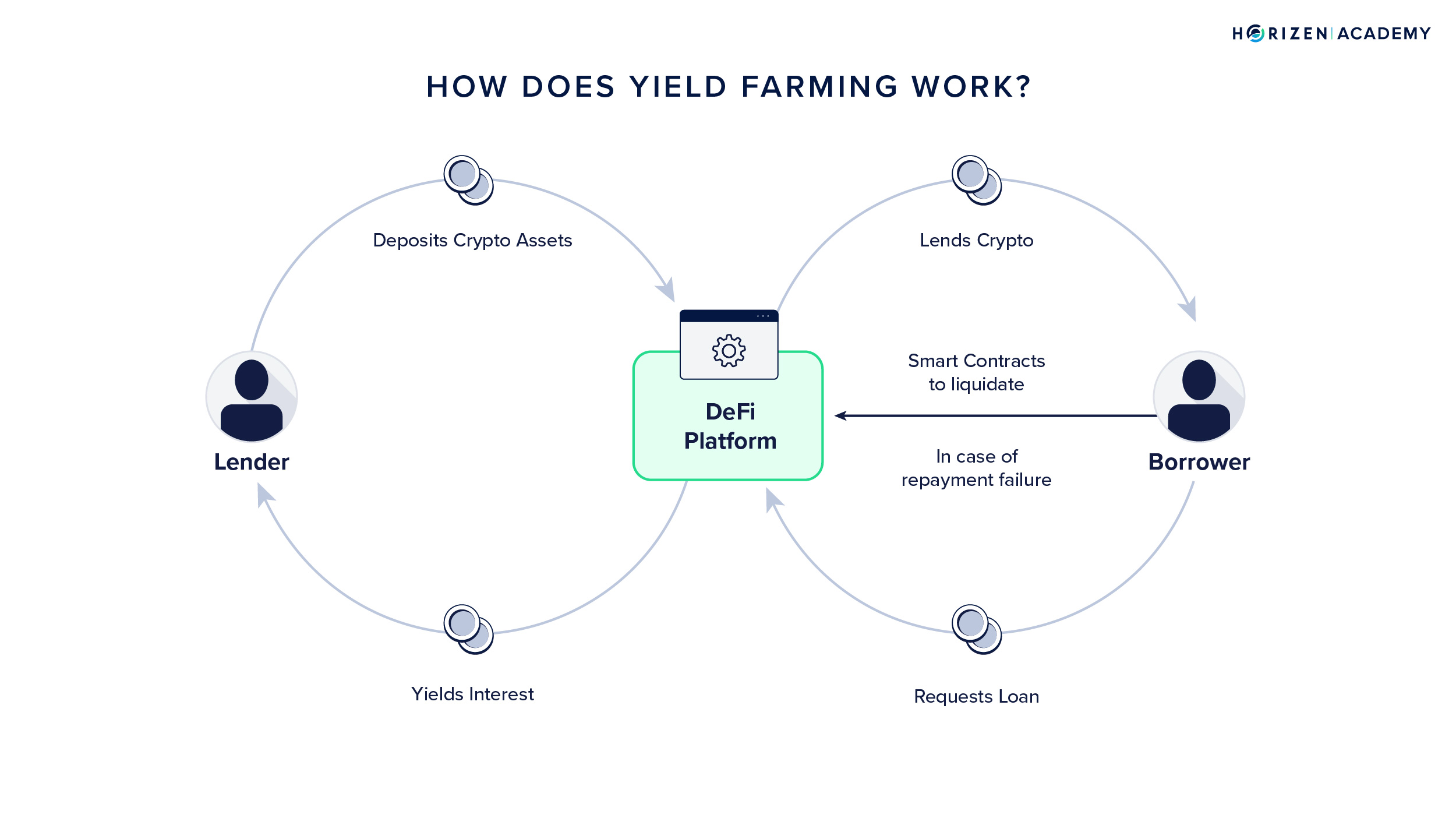
Cons:
- Complex Strategies: Often involves complex strategies that can be difficult to understand and manage.
- Market Risk: Subject to market volatility, with the potential for significant losses.
- Liquidity Risk: Some yield farming strategies can lock up assets for extended periods, affecting liquidity.
Concentrated Liquidity
Functioning:
This approach allows liquidity providers to allocate their funds to a specific price range within a liquidity pool. It offers more focused liquidity, ensuring that capital isn’t spread too thinly across a wide price range, which is especially beneficial for stablecoin pairs or assets with lower volatility.
Pros:
- Capital Efficiency: Enables higher capital efficiency by allowing liquidity providers to target specific price ranges.
- Customization: Offers the flexibility to customize strategies based on market outlook and risk tolerance.
- Potential for Higher Yields: Can result in higher yields within the targeted price range due to increased trading activity.
Cons:
- Active Management Required: Requires continuous monitoring and adjustment of price ranges to maximize returns and minimize risks.
- Risk of Being Out of Range: If the market price moves outside the chosen price range, the liquidity provided becomes inactive, and no fees are earned.
- Complexity: More complex than traditional liquidity provision, potentially deterring less experienced users.
Expanding Horizen EON's Approach to Enabling Liquidity
Horizen EON, Horizen's EVM-compatible smart contracting platform, is making significant strides in enhancing liquidity within the DeFi ecosystem. Its approach is multifaceted, aiming to create a robust and versatile environment for liquidity to thrive. Here, we delve deeper into the specific strategies and innovations that Horizen EON employs to foster liquidity.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
Auros Integration: By partnering with Auros, Horizen EON taps into algorithmic trading expertise, ensuring that the EON ecosystem and the $ZEN token benefit from enhanced liquidity. This collaboration facilitates seamless trading experiences, crucial for the growth of EON as a premier platform for DeFi activities.
Multi-ecosystem Alliances: Beyond Auros, Horizen EON seeks partnerships with other DeFi entities and blockchain projects, creating a network that supports a wide range of tokens and assets, thereby amplifying liquidity sources.
EVM Compatibility: A Gateway to Ethereum's Liquidity
Interoperability with Ethereum: EON's compatibility with Ethereum allows it to leverage the existing liquidity pools and DeFi applications of Ethereum, effectively pooling liquidity resources.
Easier Porting of DApps: Developers can port existing Ethereum DApps onto EON with minimal changes, bringing their inherent liquidity and user base along.
Advanced Smart Contract Functionality
Customizable Liquidity Pools: EON’s smart contracts enable the creation of tailored liquidity pools that can cater to specific DeFi products, allowing more targeted and efficient liquidity allocation.
Innovative Financial Instruments: EON supports the development of complex financial instruments that can attract institutional and sophisticated investors, thereby injecting additional liquidity.
Developer and Community Empowerment
Developer-Friendly Tools: By providing robust development tools and resources, EON encourages the creation of diverse DeFi applications, contributing to a more liquid and vibrant ecosystem.
Community Governance Models: Incorporating governance models that allow community participation in decision-making processes can lead to more aligned and sustainable liquidity strategies.
Future-Proofing Through Research and Development
Ongoing Innovation: Horizen EON is committed to continuous research and development to stay ahead of emerging trends and technologies in DeFi, ensuring its liquidity mechanisms remain cutting-edge.
Scalability Solutions: Recognizing the importance of scalability in liquidity provision, EON is working on solutions to ensure fast, cost-effective transactions even during high network demand periods.
Risk Management and Security Measures
Security Frameworks: EON places a high emphasis on security in its liquidity protocols to protect against vulnerabilities and ensure trust, a key factor in attracting and maintaining liquidity.
Risk Mitigation Strategies: Through smart contract audits, insurance mechanisms, and other risk management practices, EON aims to create a safe environment for liquidity providers and users alike.
Conclusion
Liquidity is the lifeblood of DeFi, determining the health and efficiency of the entire ecosystem. From AMMs to DEXs and beyond, the methods of providing liquidity continue to evolve, each with its unique advantages and challenges. Horizen EON, with its strategic partnerships, EVM compatibility, and advanced smart contract capabilities, is at the forefront of this evolution, driving liquidity and innovation in the DeFi space. As DeFi continues to grow, platforms like Horizen EON will play a crucial role in shaping its future, ensuring that liquidity remains robust and accessible for all market participants.